Glossary of Chemical Terms - H
H
- half-cell
- An oxidation or reduction reaction that occurs at an electrode.Two half-cells must be combined to form an electrochemical cell.
- half-life
- The time required for concentration of one substance to reach half of its initial value.The time it takes for one half of a substance to be metabolized and/or excreted from the body.
- half-reaction
- A reaction that shows the electrons involved in an oxidation or reduction step of a reaction.
- halide
- A negatively charged ion of the group VIIA elements.
- halogen
- The group VIIa elements in the periodic table.
- heat
- The transfer of (thermal) energy between two objects that are at different temperatures.
- Henry's Law
- The amount of gas dissolved in a solution is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the solution.
- heterocycle
- A compound containing at least one ring that consists of both carbon and non-carbon atoms .
- heterogeneous
- Describes a material or substance or chemical reaction which is not the same throughout in its properties, composition, or state of matter.
- homeopathy
- A system of disease treatment involving application of minute doses of a remedy that, in a healthy person, would produce symptoms of the disease.
- homogeneous
- Describes a material or substance or chemical reaction which is the same throughout in its properties, composition, or state of matter.
- hybridization
- A mixing process, often applied to description of atomic orbitals, producing orbitals that have characteristics intermediate between the various types of orbitals involved.
- hydrate
- A crystalline solid with molecules of water trapped in the solid state structure, which can often be removed partly or completely by relatively gentle heating.
- hydration
- Having solvent molecules of water surrounding and becoming attached to ions or molecules of the solute.
- hydrocarbon
- An organic compound containing only the elements hydrogen and carbon.
- hydrolysis
- Cleavage of a covalent bond brought about by water; the H- and -OH of water typically become attached to the respective cleavage fragments.For example:
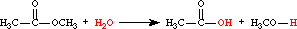
- hydrolyze
- To add hydrogen or hydroxyl to a substance.
- hypothesis
- A scientific "hunch," a tentative explanation of or prediction derived from experimentation.
Glossary created by David Shaw (Madison Area Technical College) for The Chemistry Place.
Information Please® Chemistry Place, ©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
| Contents |







