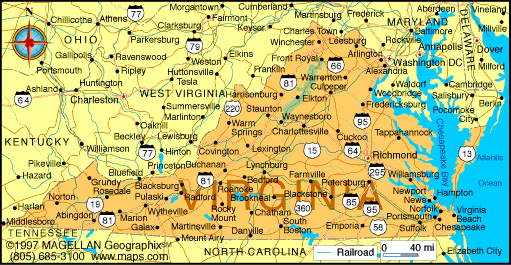
Virginia


Virginia State Information
Capital: Richmond
Official Name: The Commonwealth of Virginia
Organized as a territory: Virginia was organized as a territory on July 13, 1787.
Entered Union (rank): Virginia entered the Union as the 10th state on June 25, 1788.
Present constitution adopted: 1971 with 14 amendments
State abbreviation/Postal code: Va./VA
State Area Codes: 276, 434, 540, 703, 757, 804, 826, 948, and 571
Fun Facts About Virginia
Nickname: “The Mother of Presidents”
Origin of name: Virginia is named after Queen Elizabeth I of England, who was often referred to as the "Virgin Queen."
Motto: Virginia's motto is "Sic Semper Tyrannis," which translates to "Thus Always to Tyrants."
Slogan: Virginia does not have an official state slogan.
Anthem: Virginia's state song is "Carry Me Back to Old Virginny."
Flower: American Dogwood (Cornus florida)
Tree: American Dogwood (Cornus florida)
Animal: American Foxhound
Bird: Northern Cardinal
Fish: Brook Trout
Vegetables: Tomato and Virginia Peanut
Gem: Nelsonite
Song: "Our Great Virginia" by Mike Greenly and Jim Papoulis
Spanish language song: Virginia does not have an official Spanish language song.
Poem: "Virginia's Way" by Dr. William E. Frazier
Grass: Kentucky Bluegrass
Fossil: Chesapecten jeffersonius (a scallop shell)
Cookie: Virginia's official cookie is the Chocolate Chip Cookie.
Insect: Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly
Ballad: "The Ballad of the Old Dominion" by James Bland
Bilingual song: Virginia does not have an official bilingual song.
Government
Governor: Glenn Youngkin (R)
Lieutenant Governor: Winsome Earle-Sears (R)
Secretary of the Commonwealth: Kay Coles James (R)
General Treasurer: David L. Richardson (Independent)
Attorney General: Jason S. Miyares
Senators: Mark Warner (2009-) (D); Tim Kaine (2018-) (D)
Historical biographies of Congressional members
State website: www.virginia.gov
Population
Residents: Virginians
Resident population: 8,631,393 (2022)
10 largest cities: Virginia Beach (457,658); Chesapeake (247,172); Norfolk (238,556); Arlington (235,764); Richmond (225,676); Newport News (185,069); Alexandria (158,185); Hampton (136,748); Roanoke (99,578); Portsmouth (97,454)
Race/Ethnicity: White Alone (68.8%); Black/African Alone (20.0%); American Indian/Alaska Native Alone (0.6%); Asian Alone (7.2%); Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander Alone (0.1%); Two or More Races (3.4%); Hispanic/Latino (10.2%); White Alone, Not Hispanic or Latino (60.3%)
Religion: Christian Affiliation (73%); Evangelical Protestant (30%); Mainline Protestant (16%); Historically Black Protestant (12%); Catholic (12%); Mormon (2%); Orthodox Christian (1%); Jehovah’s Witness (<1%); Other Christian (<1%); Non-Christian Affiliations (6%); Jewish (1%); Muslim (1%); Buddhist (1%); Hindu (<1%); Other Non-Christian (1%); Unaffiliated (Religious Nones) (20%); Atheist (2%); Agnostic (4%); Nothing in Particular (15%)
Sex: Male (49.5%); Female (50.5%)
Age: Under 5 Years: 5.7%; Under 18 Years: 21.8%; 65 and Over: 16.3%. Median Age: 38.8
Economy
GDP: $498.8 billion dollars (24th in the U.S., 2022)
Unemployment Rate: 3.1% (2023)
Geography
Land area: 42,775 sq mi
Geographic center: Teresa's Place, 15055 N James Madison Hwy, Dillwyn, VA 23936, USA
Number of counties: 134 Counties
Largest county by population and area: Fairfax County (1.15 million people); Pittsylvania County (978 sq mi/ 2533.0 sq km)
State parks/recreation areas: 41 state parks, 5 State Forests, 3 National Historic Parks, and 2 National Parks.
See more on Virginia:
Encyclopedia: Virginia
Encyclopedia: Geography
Encyclopedia: Economy
Encyclopedia: Government
Encyclopedia: History
Monthly Temperature Extremes
Virginia, nicknamed “Old Dominion”, was admitted to the United States as the 10th state on June 25, 1788. The state capital is Richmond, though the largest city is Virginia Beach. Virginia is one of the original 13 colonies with the oldest settlement of Jamestown, and is famed for a variety of National and State Parks, including York River and Shenandoah.
Geography
Virginia is a fascinating place, including its geographic boundaries and landscape types.
Size and Position
Virginia is bordered by Maryland in the northeast, the Atlantic Ocean in the southeast, North Carolina and Tennessee to the south, and Kentucky, and West Virginia in the northwest. Virginia lies on the eastern coast of the United States and eventually became a bridge between the North and the South after the Civil War.
Landscape and Climate
Virginia has a humid, sub-tropical climate that sees pleasantly hot summers and mild, but crisp, winters with moderate rainfall throughout the year.
Virginia has mountain ranges, bays, and plains with very fertile soil that sprouts crops frequently. The Blue Ridge Mountain Range and the Chesapeake Bay are the main geographical highlights of Virginia. The tidewater region is the land east of the Fall Line and makes the natural border with the Piedmont region.
Virginia People and Population
Virginia has become increasingly diverse, as immigrants from all around the world have come to seek better opportunities and make Virginia their home.
Age
Per the 2022 Census, in Virginia, the larger portions of the population are showing to be under 18 with 21.5% of the population or 65 and over at 16.9%. The average age in Indiana is 38.8 years.
Gender
The gender in Virginia is pretty evenly split with 50.5 reporting as identifying female and 49.5 reporting as identifying male.
Ethnicity
Virginia has a Caucasian population of 68.8%, a Black/African American population of 20%, and a Hispanic or Latino population of 10.2%
Religion
Religion in Virginia has a majority of Christian affiliations with 73% of the population identifying as a subgroup under Christianity. Virginia also has a high rate of Religious Nones or Unaffiliated denominations with 20% of the population reporting as Atheist, Agnostic, or Nothing in Particular. The remaining percentage reported Non-Christian Affiliations (i.e. Jewish, Muslim, Buddhist, Hindu).
Health & Insurance
In 2020, health care in Indiana saw a rate of 10.1% of Virginians without insurance. Insurance provided by a public health office (such as Medicaid/Medicare) was at 26.4%.
Income
The median household income in 2021 was $80,615 with 10.2% of the population living in poverty.
Education
Virginia ranked 11th overall for education, but 14th for Higher Education and 13th for K-12. There is an 88.8% high school graduation rate, as opposed to the national average of 86.5%. The top three universities in Virginia are the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, William & Mary in Williamsburg, and Virginia Tech in Blacksburg.
Governor Youngkin has announced the “Bridging the Gap” initiative designed to address the shortcomings of public education and restore educational excellence to Virginia’s public schools.
Immigration
As of 202, 94.2% of Virginia residents were U.S. citizens. The most common birthplaces for foreign-born residents were El Salvador with 109,276 people, India with 94.596 people, and Mexico with 56,409 people. 16.4% of households in Virginia reported speaking a non-English language as the primary language in the home. Spanish, Chinese (Mandarin and Cantonese), and Korean were the most reported.
Virginia Government
Virginia's government has fully revised its constitution six times. The changes made were inspired by the perceived social and political needs that can result in economic opportunity for some and disadvantages for others. Article VII of the Constitution of Virginia provides the framework and laws for local governments.
Structure
The structure of the Virginia state government follows the set-up of the United States government set-up very closely. The Virginia General Assembly comprises a 100-member House of Delegates and a 40-member Senate. The state constitution allows the legislative branch to enact several laws, approve budgets, confirm the governor’s appointments, and elect judges and other public officials.
Much like the United States Supreme Court, the Supreme Court of Virginia has four levels of courts and operates very similarly to the federal court system.
Political Trends
Per the Pew Research Center, Virginia is trending more Conservative with 43% of the population voting in favor of the Republican presidential candidates. 51% of Catholics and Evangelical Protestants make up the Conservative population while the Liberal and Moderate populations make up 18.5% of that religious political demographic.
Virginia Economy
Virginia has a strong and diverse economy that ranks ninth in the U.S. for overall economic impact. The state’s GDP is estimated to be around $515 billion, making it one of the top 15 gross domestic product (GDP) contributors in the U.S.
Extraction Industries
According to Virginia.gov, sand, clay. limestone, granite, slate, mineral sands, vermiculite, and kyanite are minerals that are currently being mined in Virginia.
Gold, copper, arsenic, manganese, and iron, among many others, have all been mind in Virginia throughout the years.
Arts and Entertainment
Virginia has had an Arts Festival since 1997, which brings some of the world’s greatest artists to perform at venues throughout the Hampton Roads area.
Several films have been shot in Virginia and Virginia has several events for local artisans and craftworkers.
Tourism
If you like to be outdoors, The Mount Rogers Appalachian Trail Club is surely a place to stop by. Virginia has the most mileage of the Appalachians in North America with 550.3 miles of the trail.
The longest stretch of wild coastline remaining on the East Coast can be found in Eastern Shore, Virginia. There you can find the carless Tangier Islands, 14 undeveloped seaside barrier islands, an award-winning winery, and historic waterfront towns.
Washington D.C. lies in northern Virginia, where there are tons of sights to see especially if you are a history buff! Manassas National Battlefield Park is also located in this area as is Arlington National Cemetery.
Agriculture
The Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services asserts that agriculture is Virginia’s largest private industry, it brings in about $82.3 billion annually. The industry is made of crops and livestock, with livestock production bringing in roughly 63% of farm cash receipts. Virginia ranked 3rd in the U.S. states for the production of tobacco, 4th in seafood, and 6th for apples, pumpkins, and turkeys. Virginia has 41,500 farms that cover over 7,700,000 acres!
Wealth and Poverty
As of 2022, the poverty rate in Virginia is 10.2%, and the rate of extreme poverty is 6%. 9.4% of people are experiencing food insecurity and almost 23.4% of the population are working under the poverty line due to the moderate percentage of low-wage jobs. 8.8% of Virginians are uninsured.
Though 34% of Virginia rent their home, the property tax rate is relatively low in comparison to other states. The median annual property tax rate is 0.75%, compared to the U.S. national average of 0.99%. 13% of Virginian children are living in poverty and 26% of single-parent families are living below the poverty line.
The criminal justice system incarcerates 422 per 100,000 residents and 918 youths currently reside in juvenile justice and correctional facilities.
Virginia Interesting Facts
Did you know some of these fascinating tidbits that make Virginia one of the most intriguing states?
-
Virginia is home to 8 of the 46 presidents that have served the United States. Those include the United States’ first presidents George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, James Monroe, William Henry Harrison, John Tyler, Zachary Taylor, and Woodrow Wilson.
-
The first settlement of what would become the United States was in Jamestown, Virginia in 1607.
-
Jamestown is a part of the Historic Triangle which includes Colonial Williamsburg and Yorktown. These sites were crucial during the American Revolution. Yorktown, for example, is where the American Revolution formally ended.
-
In addition to amazing natural resources, Virginia is also home to the Central Intelligence Agency, and the Pentagon (the United States Department of Defense Headquarters), and holds a title for motor speedways with NASCAR.
-
The home of Thomas Jefferson, Monticello, is also located in Virginia.
-
Virginia has approximately 594 law enforcement agents for every 100,000 people.
Virginia History
History, culture, and natural beauty make Virginia an incredible place to live. Let’s discover some of the most interesting aspects of Virginia’s history!
Pre-Colonial History
The original inhabitants of Virginia arrived any time between 10,000 to 12,000 years ago. The indigenous folks that lived there were settled and grew crops such as corn, beans, and squash. Though there were several Native Americans who lived in the area, settlers mostly interacted with the Powhatan.
Colonial History
The first permanent English settlement, Jamestown, supported by the London Company, was founded in 1607 by John Smith. As opposed to the Massachusetts colonies, the Virginia colonies were founded for purely economic reasons. Colonists hoped to find gold, spices, and land to grow crops. The original settlers were a company of 104 men and boys with little to no farming ability leaving the colony at risk of starvation and native attacks. However, the natives in this area helped the colonists cultivate enough food to survive the winter and helped them through the spring.
Though the struggles were many and the native-colonist relations soured, the arrival of John Rolfe in 1612 and his development of tobacco turned the tide of the Jamestown colony.
In 1619, a newly appointed governor called for the first representative legislative assembly which was the foundation for the representative government now seen in the U.S.
The state that boasts of being the Mother of Presidents, can also boast of being the Mother of many Founding Fathers and the birthplace of the American Revolution. The First Continental Congress and the Battle of Yorktown, the final battle of the American Revolution occurred in Virginia. Thomas Jefferson who penned the Declaration of Independence, and George Washington, the United States’ first president hailed from Virginia.
Pre-Civil War History
While the state abolished the African slave trade in 1778, the institution of slavery flourished in Virginia in the early 1800s. Nat Turner, an enslaved preacher, encouraged a slave rebellion that resulted in many deaths and spread fear across the slaveholding South.
In 1861, Virginia followed South Carolina’s lead and seceded from the Union to join the Confederate States of America. Richmond became the capital of the Confederacy and Virginia became the main battleground for the American Civil War. Battles such as the battles of Bull Run, Fredericksburg, Chancellorsville, and Wilderness all were fought in Virginia.
In April 1865, at the Appomattox Court House, Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union commander Ulysses S. Grant, ending the American Civil War. The creation of West Virginia was also decided at this meeting, West Virginia entered the Union as a free state.
Post Civil War
During the Reconstruction Era, the Republican party came to the majority for a brief time. In that time, African American men were given the right to vote, education was improved, and the economy was refocused on the railroads.
Though slaves had been freed, given citizenship, and men were given the right to vote, there were extreme measures put in place to keep the freed population marginalized. The Black Codes were enforced, followed by the Jim Crow Laws.
In 1870, Virginia was formally readmitted to the Union. In the late 1870s and 1880s, the Democratic Party regained control in Virginia. The state suffered many debts and could not perform as it had promised for education, though the state did recover from the devastating debt slowly.
Virginia’s economy was still largely agricultural, with tobacco being the breadwinning crop. As the railroad expanded, so did the market for manufacturing industries such as timber, coal, textiles, and cigarettes.
Modern History
Virginia’s Constitution of 1902 authorized poll taxes, and literacy tests, and mandated separate schools based on race. As policies were written and passed into laws, Black people came together to fight for their rights. The Black community made up for the lack of proper facilities by creating their own and by the 1930s, plaintiffs filed lawsuits to break down segregation at the graduate and professional school levels. By 1951, an equalization case arose in Prince Edward County. This case, Davis v. Prince Edward County, became one of the five cases that compromised the Brown v. Board of Education decision in 1954 which overturned Plessy v. Ferguson. This was a huge step in paving the way for the Civil Rights movement.
In 1989 Douglas Wilder became Virginia’s first African-American governor. In the late 1900s, Virginia saw extensive suburban growth specifically around Washington D.C. and Richmond.
People Also Ask…
If you are interested in more information about the state of Virginia, then keep reading — we have compiled answers to the most common FAQs below. Plus, test your newfound state knowledge by taking our quiz on The Oldest U.S. States!
What is Virginia known for?
Virginia is known for its rich history and is often referred to as the birthplace of a nation. It's home to Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement, and Williamsburg, a restored colonial town. Virginia is also famous for its breathtaking natural beauty, including Shenandoah National Park and the scenic Blue Ridge Parkway.
What is the capital of Virginia?
The capital of Virginia is Richmond.
Is Virginia a good place to live?
Yes, many people find Virginia to be a great place to live due to its diverse geography, strong job market, excellent schools, and rich history.
What is the climate like in Virginia?
Virginia has a humid subtropical climate. Summers can be hot and humid, while winters range from mild to cold. The state experiences all four seasons.
What are some major cities in Virginia?
Major cities in Virginia include Virginia Beach, Norfolk, Chesapeake, Richmond, Newport News, Alexandria, Hampton, Roanoke, Portsmouth, and Suffolk.
Famous Virginia Natives and Residents
Richard Arlen actor;
Arthur Ashe tennis player;
Pearl Bailey singer;
Russell Baker columnist;
Warren Beatty actor;
George Bingham painter;
Richard E. Byrd polar explorer;
Eric Cantor political leader;
Willa Cather novelist;
Roy Clark country music artist;
William Clark explorer;
Henry Clay statesman;
Clarence Clemons musician;
Joseph Cotten actor;
Katie Couric TV newscaster;
Ella Fitzgerald singer;
William H. Harrison president;
Patrick Henry statesman;
Sam Houston political leader;
Thomas Jefferson president;
Robert E. Lee Confederate general;
Meriwether Lewis explorer;
Shirley MacLaine actress;
James Madison president;
Moses Malone basketball player;
Aimee Mann musician;
John Marshall jurist;
Cyrus McCormick inventor;
James Monroe president;
Opechancanough Powhatan leader;
John Payne actor;
Walter Reed army surgeon;
Matthew Ridgway general;
Bill "Bojangles" Robinson dancer;
George C. Scott actor;
Sam Snead golfer;
J. E. B. Stuart Confederate general;
Thomas Sumter general;
Zachary Taylor president;
Nat Turner leader of slave uprising;
John Tyler president;
Michael Vick football player;
Booker T. Washington educator;
George Washington first president;
Woodrow Wilson president;
Tom Wolfe journalist.
U.S. State Comparisons
Population & Economy
Historical Population Statistics, 1790–Present
Per Capita Personal Income
Minimum Wage Rates
State Taxes
Federal Government Expenditure
Percent of People in Poverty
Births and Birth Rates
Homeownership
Percentage of Uninsured by State